
In general, acid-alkali reactions can be boiled down to:Ī nucleophile or ligand is an ion of hydroxide. Base salts will react with acids to neutralise them. In water, base salts dissociate into a cation and one or more hydroxide ions, resulting in a basic solution. Ammonia (NH3) is one such example:īase salts are salts that contain hydroxide. As a result, hydroxide ions are involved in a wide range of acid-base reactions, including the neutralisation reaction.Īn Arrhenius base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in aqueous solution. The significant proportion of hydroxide-containing compounds are chemical bases. For example, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in an industry sector as a strong base, whereas potassium hydroxide is used in agriculture. Furthermore, hydroxides are commonly used in human activities. Many mineral ores, including bauxite ores and limonite, are hydroxides. Hydroxide compounds and ions are found abundantly in nature. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and ammonium hydroxide are common examples. The term "hydroxide" also refers to a group of compounds containing the ion hydroxide. It is one of the most fundamental diatomic ions known. The element oxygen (shown as an O) is bonded to the element hydrogen (shown as a H).
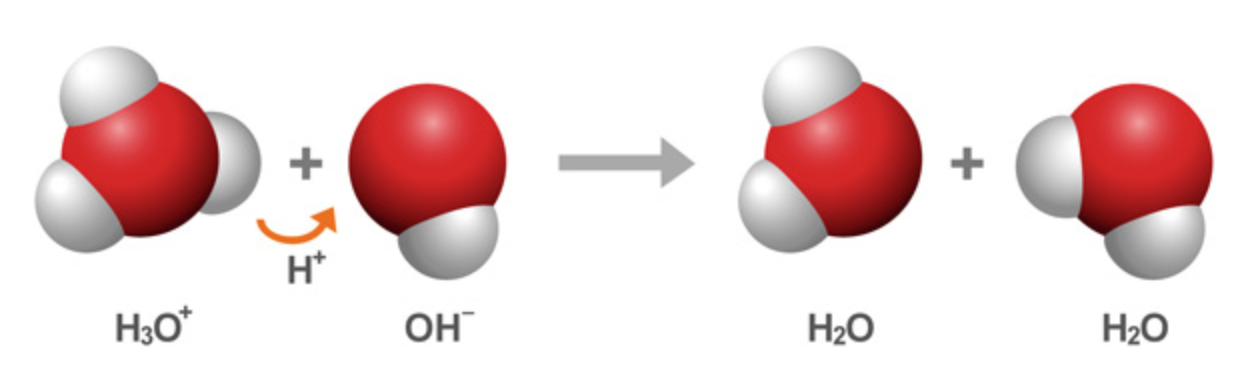
Since it has obtained an electron, hydrogen has a negative charge.
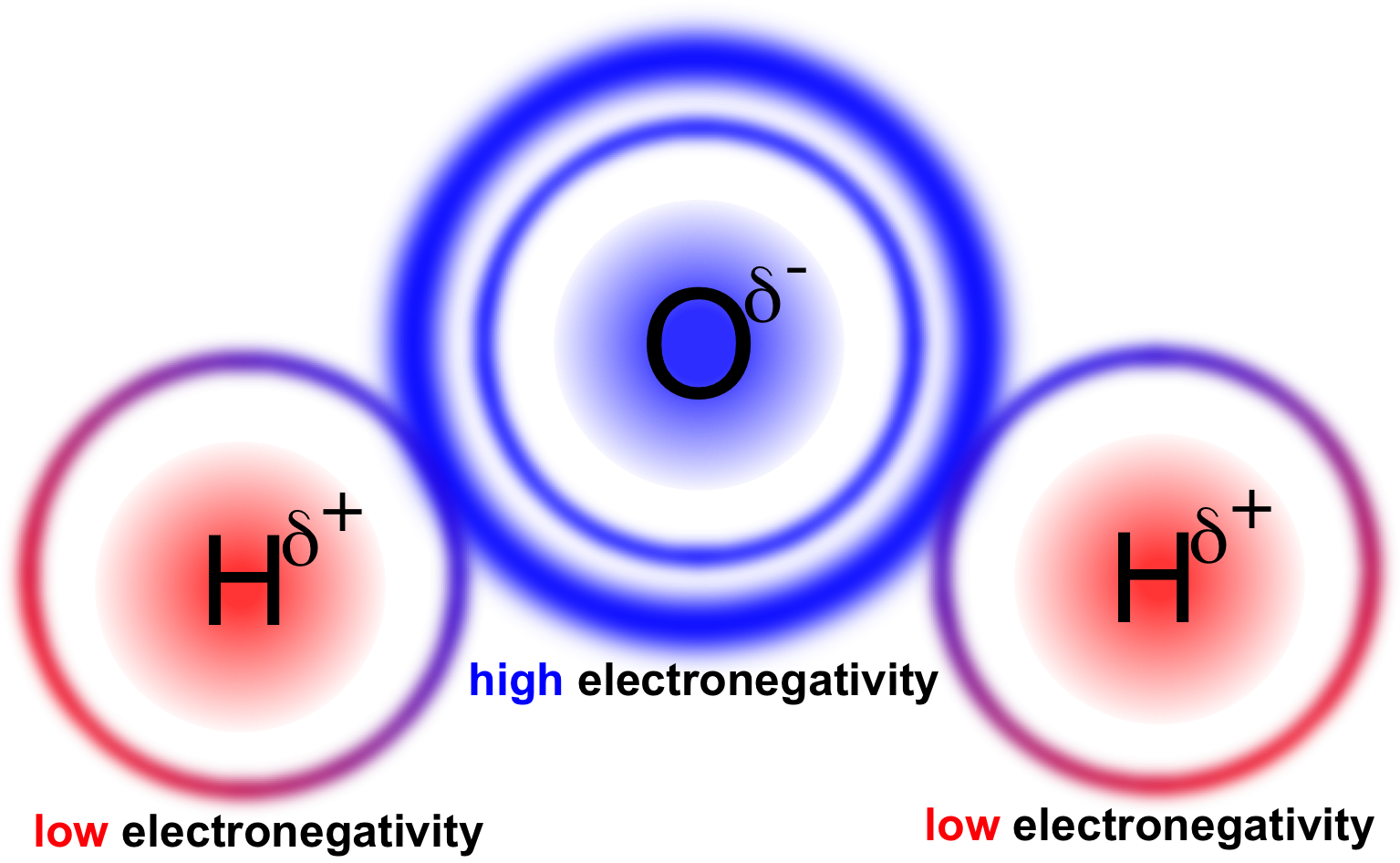
In this compound, oxygen and hydrogen form a two-electron bond. Read More : Group 18 Elements Formula of Hydroxide Hydroxide oxidanide hydridooxygenate (1−)Ī chemical composed of a positively charged ion bonded to a negatively charged ion is known as an ionic compound.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
